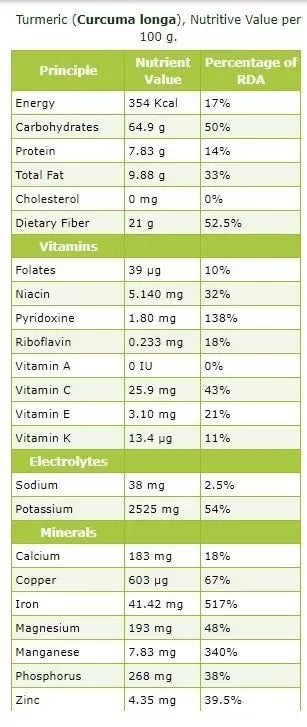
Turmeric is more than just Curcumin…
Please note: This article is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease. Results may vary from individual to individual.
Turmeric is widely used for its anti-inflammatory properties which come from the Curcumin nutrient found in the root. However, what many people don’t realise, is that Turmeric is also jam-packed with over 15 other nutrients that are extremely beneficial for our bodies.
Turmeric has been used for centuries in Ayurvedic medicine because of the combination of nutrients it possesses and their many benefits. Below we have listed these other key nutrients found naturally withinthe Turmeric root and how they assist our bodily functions.

Nutrients Found in Turmeric (Curcuma longa)
- Folate (Vitamin B9) is important because it plays a role in DNA synthesis and repair. It encourages cell and tissue growth.
- Niacin (Vitamin B3) can improve cholesterol levels and lower cardiovascular risks. Maintains skin health, supports brain function and helps joint mobility.
- Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) plays a part in such major functions such as movement, memory, energy expenditure and blood flow.
- Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) plays a major role in energy production.
- Vitamin A plays a vital role in bone growth, reproduction and immune system health as well as being essential for eye and vision health.
- Vitamin C is necessary for the growth, development, and repair of all body tissues. It’s involved in many body functions, including the formation of collagen, absorption of iron, the immune system, wound healing, and the maintenance of cartilage, bones, and teeth.
- Vitamin E works to block free radicals from the body, which play a large part in the aging process.
- Vitamin K regulates normal blood clotting as well as transports calcium throughout the body to support bone health.
- Potassium is used to treat high blood pressure and preventing stroke.
- Calcium builds and maintains strong bones as well as maintain healthy muscle and nerve function.
- Copper makes red blood cells and keeps nerve cells and your immune system healthy.
- Iron is an important component of haemoglobin, the substance in red blood cells that carries oxygen from your lungs to transport it throughout your body.
- Magnesium is crucial to nerve transmission, muscle contraction, blood coagulation, energy production, nutrient metabolism and bone and cell formation.
- Manganese aids in the formation of connective tissue, production of sex hormones and aids in fat and carbohydrate metabolism, calcium absorption, and blood sugar regulation.
- Phosphorus is another important nutrient that helps build strong bones and teeth.
- Zinc is needed for the proper growth and maintenance of the human body. It is needed for immune function, wound healing, blood clotting, thyroid function.